In addition, GAAP mandate the use of enterprise funds for the separately issued financial statement of public-entity risk pools. Public-entity risk pools also are accounted for as enterprise funds when they are included within a sponsoring government’s report, provided the sponsor is not the predominant participant in the arrangement. Intragovernmental debt is not a meaningful benchmark for future costs of benefits because it represents the cumulative total of the difference between a program’s past collections and expenditures.

Open Assets sub menu
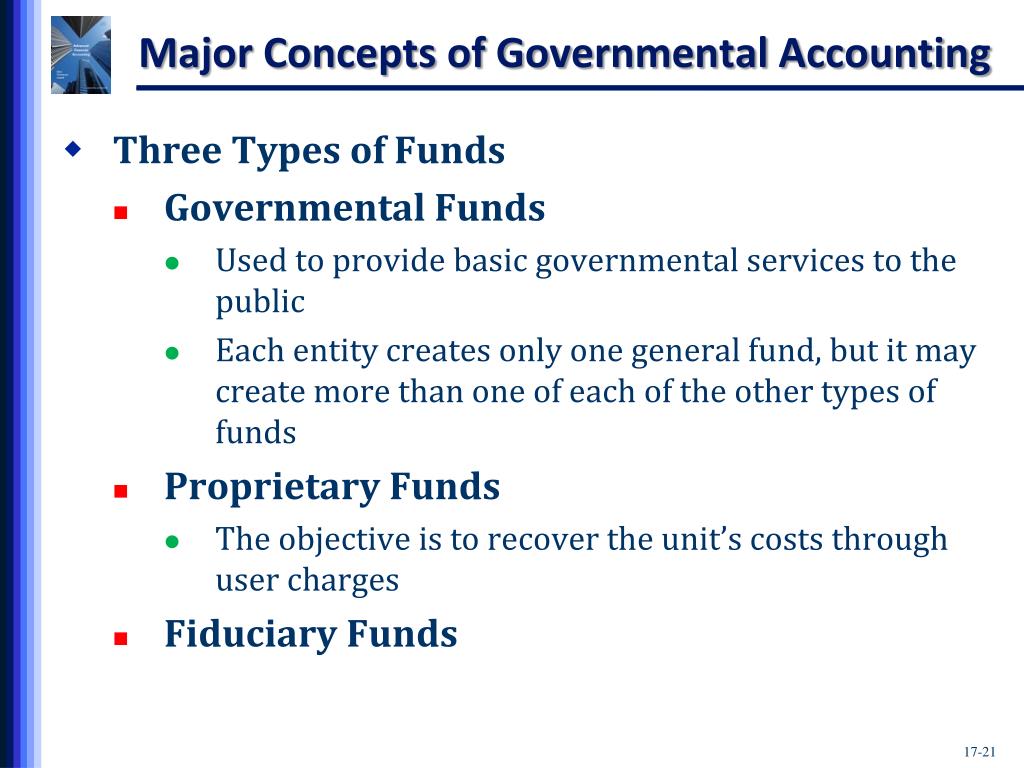
Code Internal Service Funds – may be used to report any activity that provides goods or services to other funds, departments or agencies of the government, or to other governments, on a cost-reimbursement basis. Internal service funds should be used only if the reporting government is the predominant participant in the activity. For more information on accounting for these funds see 3.9.6 and for reporting see 4.3.6. Permanent funds do not include private-purpose trust funds which account for resources held in trust for individuals, private organizations, or other governments. The state statutes contain many requirements for special funds to account for different activities. The legally required funds do not always meet GAAP standards for external reporting.
The Focus of Governmental Financial Reporting
Both criteria must be met in the same element (assets, liabilities, etc.) for a fund to be defined as major. However, GASB Statement 34 permits a government to designate a particular fund that is of interest to users as a major fund and to individually present its information in the basic financial statements, even if it does not meet the criteria. However, a government does not have the option to not report a fund as major if it meets the criteria above. Therefore, it can be seen that the governmental accounting system should be organized in a manner that ensures that all transactions are duly recorded in the system. The main premise here is to make sure that all cash or non-cash-related transactions are mentioned on the financial statement in order to reduce the chance of any embezzlement or fraudulent activities within the company.
Appropriation Categories
Addressing these challenges successfully is essential for maintaining the fiscal health and integrity of governmental operations. By examining these considerations, government officials can make informed decisions that align fund types with the financial management strategies and compliance requirements of their operations or projects. These real-world examples and decision-making insights help illustrate the practical application and importance of choosing the right fund type for efficient and effective public administration. Thus, a robust understanding of the different types of funds is fundamental for accurate accounting, effective management, and enhanced transparency in government financial operations, ultimately contributing to better governance and public service delivery. Secondly, differentiating fund types aids in effective financial reporting and decision-making. Stakeholders, including taxpayers, government officials, and financial analysts, rely on clear and accurate fund reporting to assess the financial health of the government, make informed decisions about public policies, and ensure efficient use of public resources.
- Offsetting collections are used for specific spending programs and are credited to the accounts that record outlays for such programs.
- For example, the Department of Defense incurs an obligation when it enters into a contract to purchase equipment.
- A good indicator of the activity’s significance may be comparing pledged revenues or fees and charges to total revenue.
- Capital project funds exclude those types of capital-related outflows financed by proprietary funds or for assets that will be held in trust for individuals, private organizations, or other governments (private-purpose trust funds).
With the advent of GASB 87, governmental reporting entities are now required to capitalize all leases falling under the guidance as finance leases and recognize both a lease liability and a right-to-use lease asset. For all the subsequent entries, it can be seen that all journal entries are duly recorded in terms of ensuring that all commercial activities are recorded in a proper manner. All respective accounting entries are supposed to be recorded so that they are not missed out upon. Therefore, these journal entries are maintained following which financial statements are subsequently drawn for all the respective years.
Therefore, these accounts should be properly maintained in proper compliance with the stated rules and regulations, in order to ensure that all the respective tasks and objectives are properly accounted for. The treatment of these funds on the balance sheet is similar to that of any reserve that is undertaken by commercial companies. However, what needs to be inculcated is the fact that it is supposed to be maintained on a perpetual basis because at the end of the day, government accounts also undergo an auditing treatment.
The type of fund not only dictates the accounting practices but also deeply influences fiscal management strategies and broader public policy decisions. The distinction among these funds helps ensure that resources are used appropriately, liabilities are managed effectively, and financial types of governmental funds activities are aligned with the governmental entity’s goals and legal responsibilities. In fund financial statements, governments should report governmental, proprietary, and fiduciary funds to the extent that they have activities that meet the criteria for using these funds.
Individual and institutional investors can also place money in different types of funds with the goal of earning money. Governments use funds, such as special revenue funds, to pay for specific public expenses. This article serves as an introduction to fund accounting for entities reporting under the Governmental Accounting Standards Board (GASB). Government reporting entities whose portfolio consists of leases that fall in scope for GASB 87 reporting will be required to recognize a lease asset and liability if they are the lessee, or a receivable and corresponding deferred inflow of resources as a lessor. If capturing the activity within the governmental fund, a conversion entry will be necessary at year-end to convert from the modified accrual accounting to the required full accrual for the government-wide financials.